The efficacy of interspinous spacers, as indicated by patient recovery and long-term device performance, is an essential aspect of spinal surgery outcomes. Evaluating this success entails a thorough analysis of post-operative data and recurrence of symptoms. While material selection for the spacer, such as titanium or PEEK, plays a significant role, it is also important to take into account personalized patient care and novel technological advancements. As we probe further into this topic, it becomes clear that achieving high success rates is a multifaceted endeavor requiring ongoing research and innovation.
Understanding Interspinous Spacers
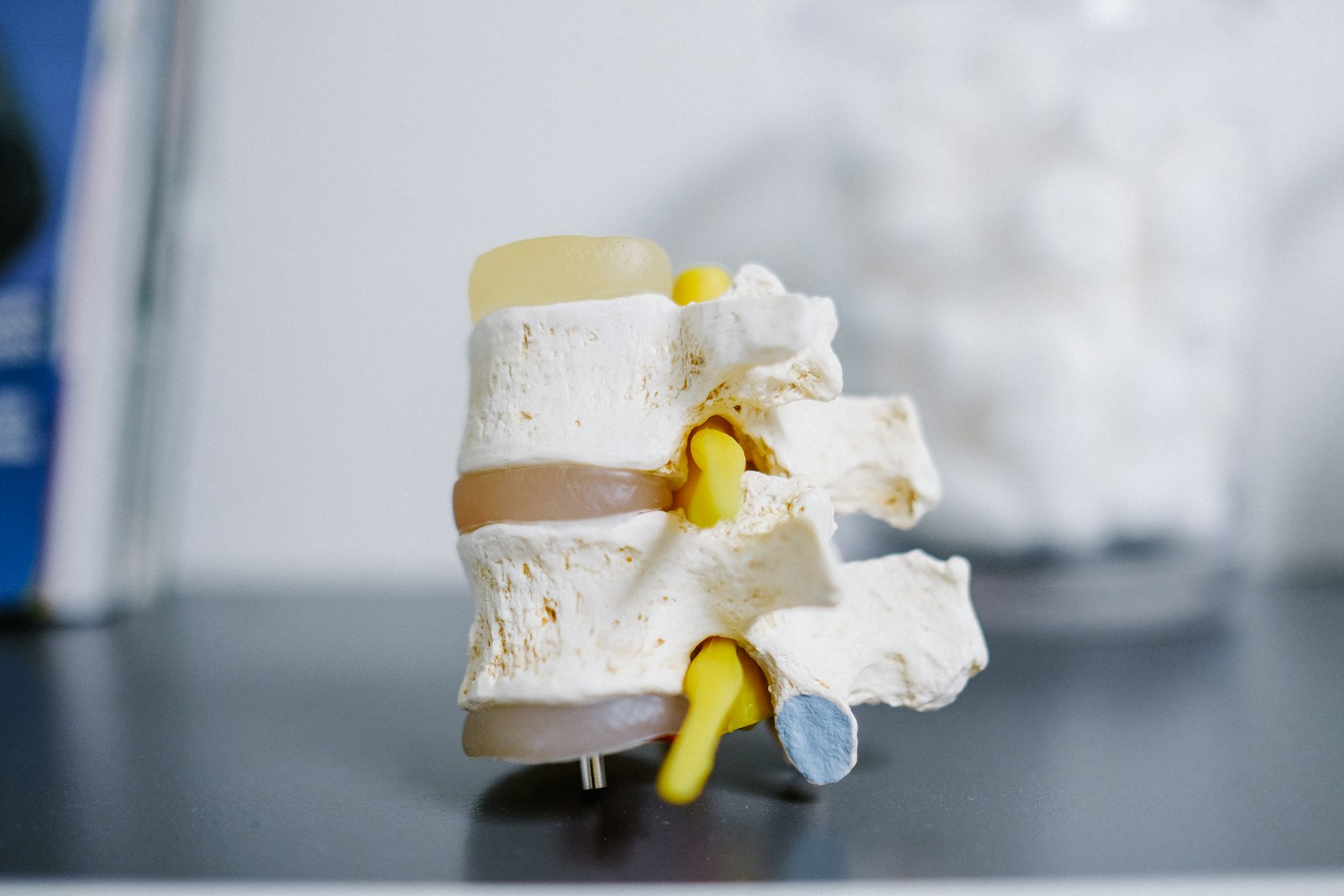
To comprehend the efficacy of interspinous spacers, one must first understand their fundamental structure and purpose in spinal surgery. These devices, typically made from durable, biocompatible spacer materials such as titanium or cobalt-chromium alloy, are designed to be placed between the spinous processes of the vertebrae. The primary goal of these spacers is to alleviate painful symptoms caused by conditions such as lumbar spinal stenosis by maintaining an ideal distance between the vertebrae, effectively decompressing the spinal canal and neural foramina.
The selection of spacer materials is critical, not only for their mechanical properties but also for their biocompatibility, which ultimately influences the success rate of the surgery. Titanium, for instance, is often chosen for its strength, lightness, and resistance to corrosion, whereas cobalt-chromium alloy offers superior wear resistance and strength.
However, the use and efficacy of interspinous spacers are often subject to insurance coverage. It is essential for patients and healthcare providers to understand the insurance implications, as not all policies cover this type of spinal surgery. This financial aspect can have a significant impact on the accessibility and feasibility of the procedure for many patients. Hence, it’s a critical component in the overall evaluation of interspinous spacers’ effectiveness.
The Surgical Procedure Explained
How is the surgical procedure involving interspinous spacers performed? The process commences with thorough surgical preparation, ensuring a sterile environment to minimize the risk of infection. The patient is placed in a prone position under general anesthesia, and a midline incision is made over the interspinous process.
Patient eligibility is an important factor. This procedure is primarily recommended for patients suffering from lumbar spinal stenosis, who have not found relief from conservative treatments. A detailed medical history is taken, and imaging studies such as MRI or CT scan are carried out to confirm the diagnosis and pinpoint the affected vertebrae.
Once the affected area is exposed, the interspinous ligament is partially removed to create space for the spacer. The device is then inserted between the spinous processes of the vertebrae. Precise placement is essential to ensure excellent functionality and alleviate the patient’s symptoms. The incision is then sutured closed, and the patient is moved to recovery.
Post-procedure, patients are closely monitored for any complications. Regular follow-ups are scheduled to assess the success of the operation and the patient’s overall improvement. This detailed, systematic approach contributes significantly to the high success rate of interspinous spacer surgeries.
Key Benefits of Interspinous Spacers
Building upon the surgical procedure, the use of interspinous spacers provides numerous benefits that greatly contribute to patient recovery and quality of life post-surgery. The advantages include relief from pain, improved mobility, and a substantial reduction in the need for additional surgical interventions.
One of the key benefits of interspinous spacers is their cost-effectiveness. Compared to other surgical interventions, the use of spacers often results in shorter hospital stays and faster recovery times, which greatly reduces the overall cost burden for both patients and healthcare systems. Additionally, these spacers can be a more affordable option for patients who may not have the means for more expensive procedures.
Another remarkable advantage lies in the material options available for spacers. These include titanium, cobalt-chrome, and polyetheretherketone (PEEK). Each of these materials has its own unique set of benefits. Titanium is known for its strength and durability, while cobalt-chrome offers superior wear resistance. PEEK, on the other hand, is radiolucent, which allows for clear imaging post-surgery.
Risks and Complications
While interspinous spacers have shown promising results, it is imperative for us to explore the potential risks and complications associated with this procedure. This discussion will encompass potential surgical complications, post-procedure risks, and strategies for managing adverse outcomes. Thorough comprehension of these facets is vital to guarantee excellent patient care and outcomes.
Potential Surgical Complications
Despite the thorough success rate of interspinous spacer procedures, potential surgical complications, such as infection, blood clots, nerve damage, or problems with the spacer itself, should be considered and discussed with patients prior to surgery. Understanding the surgical recovery timeline is crucial in mitigating these risks. Immediate postoperative days require diligent infection control measures, while long term recovery phase involves regular follow-up and monitoring for any signs of nerve damage or spacer dislocation. Pain management strategies also play an essential role in surgical recovery. Proper pain control not only enhances patient comfort but also prevents complications like blood clots that could arise from immobility due to pain. Therefore, a thorough approach to managing potential surgical complications is necessary for success.
Post-Procedure Risks
Invariably, any surgical procedure, including the implantation of an interspinous spacer, carries with it certain risks and potential complications that may arise after the operation. Notable among these are infection, bleeding, nerve damage, and spacer migration. In rare instances, hardware fractures can occur, adding to the overall spacer cost. Post-surgery lifestyle changes are also necessary to facilitate recovery and minimize risks. These might include physiotherapy, medication adjustments, and lifestyle modifications such as quitting smoking. Patients may also experience temporary or permanent changes in their ability to perform certain physical activities. It is essential that prospective patients understand these risks and engage in a detailed discussion with their healthcare provider to make an informed decision about the procedure.
Managing Adverse Outcomes
Efficient management of adverse outcomes, such as infection, bleeding, nerve damage, and spacer migration, post-interspinous spacer implantation, demands a thorough, patient-specific approach involving experienced healthcare professionals. The choice of spacer material plays a vital role in minimizing complications. Biocompatible materials reduce the risk of infection and foster better tissue integration, minimizing spacer migration. In cases of bleeding or nerve damage, immediate intervention and careful follow-up are essential. Establishing a realistic recovery timeline after surgery also aids in managing adverse outcomes. Regular physiotherapy, patient education, and monitoring aid in early identification of complications, allowing for timely intervention. Overall, successful management of adverse outcomes lies in an individualized approach, expertise, and proactive patient care.
Assessing the Success Rate
To accurately evaluate the success rate of interspinous spacers, it is essential to examine both the immediate outcomes of the procedure and its long-term efficacy. This involves a thorough analysis of post-operative data, including patient recovery timelines and recurrence of symptoms. Moreover, long-term efficacy rates provide insightful information about the spacer’s performance and durability over extended periods, contributing greatly to the overall success assessment.
Spacer Procedure Outcomes
When evaluating the success rate of the interspinous spacer procedure, it is important to consider both the reduction in patient’s pain and the enhancement in their overall functionality. The spacer material, typically composed of biocompatible titanium or PEEK, plays a significant role in the procedure’s success. This material’s durability and compatibility with the human body can impact the patient’s recovery timeline and the long-term efficacy of the procedure. Post-operative outcomes are generally positive, with patients reporting significant reductions in back pain and improvements in daily activities. However, these outcomes can vary depending on the individual’s health status, the severity of their spinal condition, and their adherence to post-operative care guidelines. Therefore, a thorough evaluation of the procedure’s success must include both subjective patient-reported outcomes and objective clinical assessments.
Long-term Efficacy Rates
Evaluating the long-term efficacy rates of the interspinous spacer procedure offers a thorough understanding of the treatment’s enduring success and its impact on patient quality of life. Continuous developments in spacer material innovations have greatly influenced these rates.
The following points outline this in detail:
- Spacer Material Innovations: Advances in materials used for spacers have improved the durability, thereby enhancing the long-term efficacy rates.
- Comparative Efficacy Studies: Various studies comparing different spacer materials and surgical techniques have provided valuable insights into optimizing long-term success.
- Patient Quality of Life: Long-term efficacy is also gauged by the sustained improvement in the patient’s quality of life.
- Follow-up Duration: The extended follow-up period is essential in determining the enduring success of the procedure. The longer the follow-up, the more reliable the efficacy data.
Reviewing Relevant Clinical Studies
Exploring the world of clinical studies offers valuable insights into the efficacy and success rates of interspinous spacers. Various studies have been conducted to evaluate the effectiveness of different spacer materials and varying patient demographics on the success rate of these devices.
One such study focused on the use of spacers made from PEEK (polyetheretherketone) and titanium. Both materials showed significant efficacy in relieving symptoms associated with lumbar spinal stenosis. However, the titanium spacers displayed a slightly higher success rate, attributed to their rigid structure providing better spinal stability.
Regarding patient demographics, studies have shown that the success rates differ across age groups, sexes, and with the presence of comorbidities. In general, younger patients without significant comorbidities tend to have a higher success rate compared to older patients with multiple health issues. The research also shed light on gender differences, suggesting that males and females respond differently to the treatment, which may be attributed to anatomical differences.
All these findings underscore the importance of considering both the spacer materials and patient demographics when planning for interspinous spacer implantation. It is essential to tailor the treatment to meet the individual needs of each patient to optimize the success rate of the procedure.
Expert Opinions on Spacer Efficacy
In the nexus of medical expertise, there exists a robust discourse regarding the efficacy of interspinous spacers in managing spinal stenosis symptoms. Particularly, the prevailing expert opinions gravitate towards endorsing spacers due to their evolutionary design and cost-effectiveness.
- Spacer Cost Effectiveness: Medical professionals often highlight the cost-effectiveness of interspinous spacers. Compared to traditional surgical options, spacers provide a less invasive and more affordable alternative, leading to reduced hospitalization time and associated costs.
- Spacer Design Evolution: The design of interspinous spacers has evolved significantly over time, enhancing their functionality and efficacy. Experts appreciate this evolution as it has greatly improved patient outcomes, especially in terms of pain reduction and mobility improvement.
- Efficacy in Symptom Management: Experts affirm that interspinous spacers effectively alleviate symptoms of spinal stenosis. While they may not be a panacea, their symptom management efficacy is well-regarded in the medical community.
- Suitability for a Variety of Patients: Experts note that spacers’ versatility makes them a suitable solution for a broad spectrum of patients, including those who may not be ideal candidates for more invasive procedures. This versatility further bolsters their cost-effectiveness and overall efficacy.

Personal Patient Experiences
Shifting from expert opinions, we now direct our focus to the personal experiences of patients who have undergone the placement of interspinous spacers. A collective evaluation of patient testimonials reflects a general trend of satisfaction with the procedure’s outcomes.
Patients frequently report a significant reduction in back pain post-procedure, allowing them to return to their daily activities with minimal discomfort. These experiences are a confirmation of the spacer’s ability to alleviate spinal stenosis symptoms, thereby improving the quality of life for these individuals. The personal accounts also highlight the safety and minimal invasiveness of the procedure, which contribute to its growing appeal.
Of particular note is the reported spacer longevity. Many patients have shared experiences of prolonged symptom relief, indicating that these devices can effectively maintain intervertebral space over extended periods. However, it’s also important to note that a minority of patients reported a need for subsequent surgical intervention due to spacer migration or device failure.
These personal patient experiences, therefore, offer invaluable insights into the real-world success of interspinous spacers, echoing the positive viewpoints held by many medical experts.
Alternatives to Interspinous Spacers
While the experiences of patients highlight the efficacy and advantages of interspinous spacers, it is important to also consider other therapeutic strategies that may serve as viable alternatives to this procedure. These alternatives may offer comparable relief from symptoms, potentially at a lower spacer cost or with more favorable insurance coverage.
- Conservative Treatments: Non-surgical approaches such as physical therapy and pain management protocols can be effective for managing symptoms of spinal stenosis. These treatments may be covered by insurance and typically cost less than surgical options.
- Laminectomy: This surgical procedure involves removing part of the vertebrae to create more space for the spinal cord and nerves. While more invasive, it may offer a more permanent solution and is often covered by insurance.
- Spinal Fusion: This surgical technique is used to join two or more vertebrae together to prevent movement that causes pain. It is a more complex and costly procedure but may be an option for patients with more severe conditions.
- Disc Replacement Surgery: This involves replacing a damaged disc with an artificial one. This surgery may have a high upfront cost, but can provide long-term relief and may be covered by insurance.
These alternatives should be thoroughly discussed with a healthcare provider to determine the best course of action.
Making the Decision: Factors to Consider
Finding the way to ideal spinal health requires thoughtful evaluation of different factors before deciding on the most appropriate treatment method. The decision to proceed with the insertion of an interspinous spacer, thus, should be made after careful evaluation of various factors, including the patient’s physical health, patient’s lifestyle, and physician’s recommendation.
A critical aspect to take into account is the financial implications. The cost of interspinous spacer surgery can be substantial, potentially creating a financial burden for the patient. It is important to understand all cost implications, including those of pre-operative tests, the surgery itself, and post-operative care and rehabilitation.
Insurance considerations also play a significant role in the decision-making process. Different insurance providers offer varying coverage levels for spinal procedures. Some may cover the entire cost, while others may only provide partial coverage or none at all, depending on the policy terms and conditions. Therefore, patients must thoroughly review their insurance policies and discuss potential costs with their healthcare providers before making a final decision.
Ongoing Research and Future Prospects
The domain of interspinous spacer research is persistently evolving, with current studies primarily focusing on improving the success rate of this device. Advancements in spacer technology are continually being explored, which promise to enhance the effectiveness and safety of this treatment modality. These developments also provide a glimpse into the future implications and opportunities for patients suffering from lumbar spinal stenosis.
Current Research on Interspinous Spacer
Ongoing research in the field of interspinous spacers is paving the way for innovative advancements and uncovering promising prospects for the future. The primary focus is on spacer material innovations and understanding global market trends.
- Spacer material innovations: Research efforts involve developing materials that provide better support and durability, while minimizing complications. Biomaterials, for instance, are gaining attention for their potential to enhance osseointegration and biocompatibility.
- Global market trends: A thorough analysis of the market trends is essential for predicting future demands and challenges.
- Clinical trials: These play an important role in evaluating the efficiency and safety of new interspinous spacers.
- Patient outcomes: Studies are focusing on long-term impacts of spacers on patient’s quality of life and functionality. This research will help refine future designs and surgical techniques.
Advancements in Spacer Technology
Building on the exploration of interspinous spacer material innovations and market trends, there is substantial progress being made in the domain of spacer technology, with research studies and clinical trials paving the way for remarkable advancements and future prospects. State-of-the-art spacer materials such as titanium and polyetheretherketone (PEEK) have shown promising results regarding biocompatibility, durability, and patient outcomes. Efforts are also being made to optimize the design and manufacturing processes of these spacers to guarantee a more precise fit and enhanced stability. Additionally, a robust cost analysis is being conducted to balance the trade-off between advanced technology and healthcare affordability. These advancements are poised to greatly enhance the success rate of interspinous spacers, offering potential breakthroughs in spinal surgery.
Future Implications and Opportunities
With the ever-evolving technological landscape, future implications and opportunities within the domain of interspinous spacer technology present a compelling area of study, promising substantial advancements in spinal surgery procedures and patient outcomes.
- Spacer affordability: As research progresses, cost-effective manufacturing processes might be discovered. This could lead to a decrease in the price of spacers, making them more affordable for a larger patient population.
- Global accessibility: Improved spacer technology may facilitate distribution across the globe, particularly in developing countries with limited access to advanced medical technology.
- Technological advancements: Future research may lead to the development of spacers with even higher success rates and fewer complications.
- Patient outcomes: As spacers become more effective and accessible, patient outcomes may greatly improve, leading to a better quality of life post-surgery.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is the Typical Recovery Period After Interspinous Spacer Surgery?
The typical recovery period after interspinous spacer surgery ranges from several weeks to a few months. This timeframe can be influenced by factors such as pain management strategies and post-surgery nutritional support.
How Much Does an Interspinous Spacer Procedure Cost on Average?
The cost of an interspinous spacer procedure varies greatly, influenced by factors such as spacer material options and the surgeon’s expertise. On average, the price can range from $15,000 to $50,000.
Can I Perform Regular Physical Activities Post-Surgery?
Post-surgery implications vary, but many patients can resume regular physical activities after a recovery period. However, lifestyle adjustments may be necessary depending on individual conditions. Always consult your surgeon for personalized advice.
Are There Any Specific Exercises for Rehabilitation After the Procedure?
Yes, specific exercises after the procedure can aid in rehabilitation. However, alongside these, post-surgery nutrition is vital. Be vigilant for any spacer related complications and consult your physician for personalized exercise recommendations.
Will My Health Insurance Cover the Costs of the Interspinous Spacer Procedure?
Coverage for the interspinous spacer procedure relies on your insurance criteria. Confirm through the pre-authorization process to ensure the procedure is included in your health insurance plan’s list of covered treatments.

