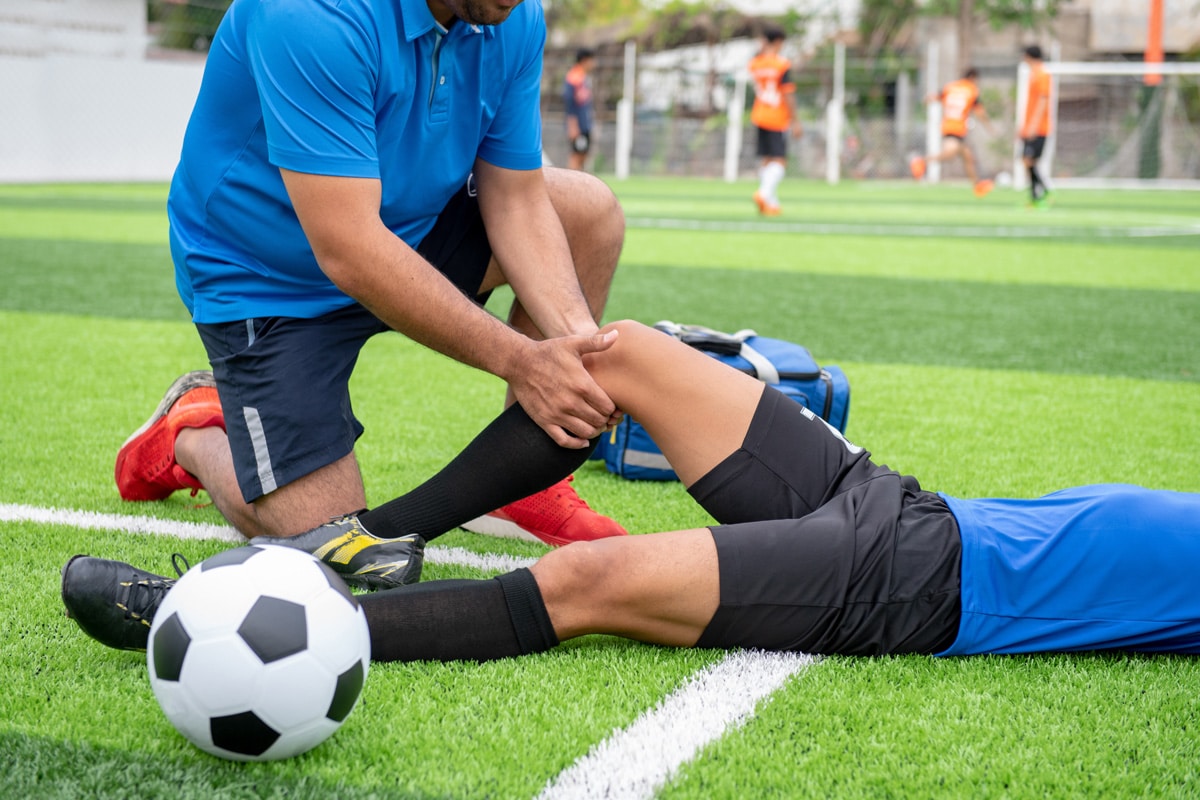
In the realm of athletic endeavor, the occurrence of sports injuries is unfortunately all too common. Such injuries, ranging from ankle sprains and knee injuries to more severe conditions like fractures and dislocations, not only hinder performance but also pose significant health risks. In order to minimize these risks, it is essential to comprehend the nature, causes, and treatments of these common injuries. However, the question remains – how can we mitigate such injuries while pursuing our athletic passions? A detailed exploration of this critical health issue awaits your attention.
Understanding Sports Injuries
Frequently occurring in both amateur and professional sports, sports injuries are a pervasive issue that require a comprehensive understanding for effective prevention and treatment. The complexity of these injuries extends beyond physical damage, delving into the realm of injury psychology, a critical component of the healing process.
Injury psychology explores the mental and emotional impact of sports injuries, acknowledging the psychological distress that often accompanies physical trauma. Coping mechanisms, resilience, and mental fortitude are key to overcoming the psychological barriers that can impede recovery.
Simultaneously, rehabilitation techniques play a pivotal role in the recovery journey. These techniques, tailored to the specific injury and athlete’s physical condition, aim to restore function, improve mobility, and alleviate pain. These measures range from physical therapies to surgeries, depending on the severity and nature of the injury.
In essence, understanding sports injuries necessitates a holistic approach that encompasses both physical and mental aspects. It requires an informed perspective that appreciates the interplay between the body and mind in injury recovery, and an analytical approach that can devise and implement effective rehabilitation strategies. This comprehensive understanding forms the bedrock of preventive measures and treatment protocols in sports medicine.
Ankle Sprains: A Closer Look
Ankle sprains, a common injury among athletes, warrant detailed examination due to their potential to sideline players. The causes of such injuries, varying from a misstep to high-impact collision, are multifaceted and often preventable. It is crucial, therefore, to explore not only their treatment options but also effective strategies for prevention.
Causes of Ankle Sprains
In the realm of sports injuries, the root causes of ankle sprains often stem from abrupt twists or turns, missteps on uneven surfaces, or athletic moves executed incorrectly. Understanding ankle anatomy is crucial to appreciating how these actions can lead to injury. The ankle is a complex structure of bones, ligaments, and muscles, which, when subjected to unexpected or unnatural forces, can result in a sprain. Such forces often occur in sports, particularly those involving rapid changes in direction or jumping. The severity of a sprain can vary depending on the degree of ligament damage. Ultimately, a thorough understanding of these causes is the first step in sprain rehabilitation, helping to design effective recovery strategies and minimize future injury risks.
Treatment and Prevention
Addressing the pivotal issue of treatment and prevention, it is critical to note that effective management of ankle sprains hinges on a multifaceted approach that includes immediate medical attention, appropriate physical therapy, and proactive preventative measures. The first step in injury rehabilitation is a thorough medical assessment to determine the severity of the sprain. This will guide the subsequent therapeutic interventions.
Physical therapy is crucial for restoring strength, flexibility, and balance, thereby minimizing the risk of recurrent sprains. Nutrition impact cannot be overlooked, as a diet rich in proteins, vitamins, and minerals promotes tissue healing. Preventative measures include wearing appropriate footwear and engaging in exercises that enhance ankle stability. An integrated approach ensures optimal recovery and reduces the likelihood of future sprains.
Knee Injuries: ACL and Meniscus
One of the most common and debilitating injuries in sports involves the knee, specifically the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) and meniscus. These injuries often occur during high-impact or twisting movements, common in sports such as football, basketball, or skiing. ACL and meniscus injuries can lead to significant pain, reduced mobility, and, in the long term, may even predispose individuals to developing osteoarthritis after injury.
There are three critical aspects to consider in managing and preventing these injuries:
- Early Diagnosis: Swift and accurate diagnosis is key to effective treatment. An MRI scan is often used to confirm the injury and determine its severity.
- Treatment Options: Depending on the extent of the injury, treatment can range from physiotherapy to surgical intervention. Knee rehabilitation exercises are vital in restoring strength and functionality to the injured knee.
- Prevention Strategies: Implementing strength training, flexibility exercises, and proper technique can significantly reduce the risk of these injuries.
Hamstring Strains: What to Know
Shifting our focus from the knee to the back of the leg, hamstring strains present another significant concern in the realm of sports injuries. These strains are common in sports that require a high degree of speed, power, and agility, such as soccer, basketball, and track and field. Understanding the hamstring anatomy is crucial to appreciate the nature of this injury. The hamstring is a group of three muscles in the back of the thigh that aid in knee flexion and hip extension.
Hamstring strains typically occur when these muscles are overstretched or subjected to excessive force. Symptoms can range from a sharp, sudden pain during exercise to a persistent dull ache. A key component of managing this injury is the implementation of rehabilitation exercises, which are designed to restore flexibility, strength, and function to the affected area.
These exercises should be graduated, starting with gentle stretching and gradually progressing to strength and conditioning exercises. The goal is to return the athlete to their pre-injury level of function while minimizing the risk of re-injury. Implementing a proper warm-up routine and improving muscle conditioning can also aid in preventing hamstring strains. It’s crucial to consult with a healthcare professional for a personalized treatment plan.
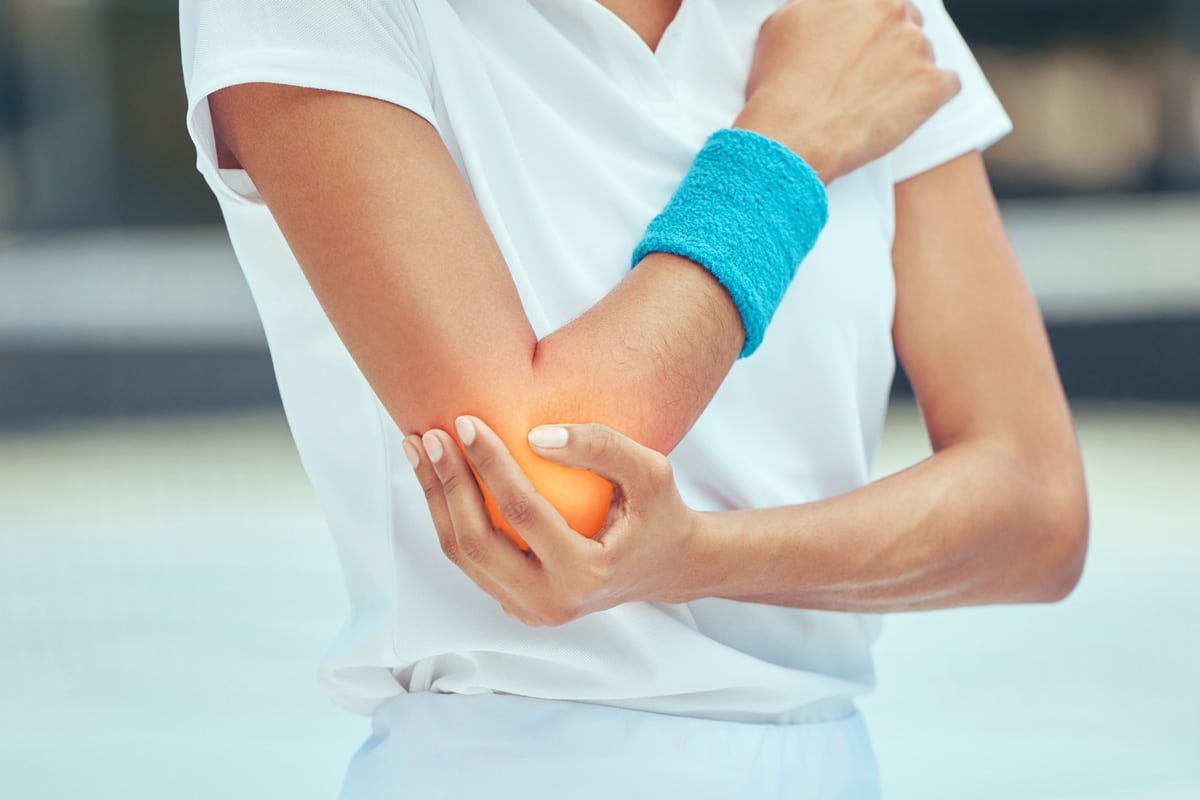

Tennis Elbow: Causes and Symptoms
Moving on to the realm of upper body sports injuries, Tennis Elbow, clinically known as lateral epicondylitis, is a prevalent condition often borne from the repetitive stress and strain of racket sports. It is characterized by pain and tenderness in the outer part of the elbow, which may extend into the forearm and wrist.
This condition primarily affects athletes, but it can also occur in individuals whose occupations or hobbies involve repetitive arm movements. Tennis Elbow is typically triggered by overusing the forearm muscles and tendons, leading to small tears in the tendons that attach to the lateral epicondyle, the bony bump on the outer part of the elbow.
- Elbow Braces: These devices can help reduce symptoms by resting the muscles and tendons. They apply pressure to the area to help alleviate pain and prevent further injury.
- Rehabilitation Exercises: Specific exercises can strengthen the forearm muscles, enhance flexibility, and increase the range of motion in the elbow joint.
- Symptoms: Common symptoms include pain and tenderness in the outer elbow, stiffness, a weak grip, and aching in the forearm.
Early diagnosis and appropriate management of Tennis Elbow are crucial to prevent chronic problems and ensure a timely return to sport or activity.
Shin Splints: Prevention and Treatment
Shin splints, a common ailment among athletes, warrant attention due to their potential to sideline active individuals for significant periods. A detailed understanding of the condition is crucial, not only for effective treatment but also for prevention. We will now explore the fundamental aspects of shin splints, discussing preventative measures and highlighting the most effective treatment methods.
Understanding Shin Splints
Often experienced by athletes, shin splints are a common, albeit painful, result of excessive stress on the shinbone and the connective tissues that attach muscles to this bone. Understanding the basics of shin anatomy can provide insight into the cause of this condition.
- Shinbone (Tibia): This is the larger of the two bones in the lower leg and bears most of the body’s weight. Overuse or strain on this bone can lead to inflammation and pain, resulting in shin splints.
- Connective Tissues: These tissues attach muscles to the shinbone. Excessive stress or force on these tissues may cause shin splints.
- Running Footwear Impact: The type of footwear used during running significantly influences the stress exerted on the shinbone and surrounding tissues. Poorly fitting or unsupportive shoes may increase the risk of shin splints.
Preventing Shin Splints
To mitigate the occurrence of shin splints, it is essential to understand the preventive measures and appropriate forms of treatment. Incorporating shin conditioning exercises can significantly reduce the risk of developing this painful condition. These exercises are designed to strengthen the muscles, tendons, and bones in the shin area, thus providing a strong support system and reducing the strain during physical activities.
Despite the benefits, there are several shin splint myths that can mislead individuals. One common myth is that shin splints are an inevitable result of running. This is misleading as the condition is often due to overuse, improper footwear, or a lack of conditioning. Therefore, with appropriate preventive measures, shin splints can be avoided.
Treating Shin Splints
While prevention is crucial, it is equally important to understand the effective treatment options for shin splints should the condition arise. Splints rehabilitation involves a series of carefully structured exercises, while taping techniques provide support and alleviate stress on the affected area.
- Rest: Giving the body adequate time to heal is paramount. This means reducing or even stopping the activity causing the pain until symptoms subside.
- Physical Therapy: This involves specific exercises that strengthen the muscles around the shin to help prevent future occurrences.
- Taping Techniques: These provide support to the affected area, reducing strain on the shin, and can be an effective part of a comprehensive treatment plan.
These steps, combined with anti-inflammatory medications, can help manage and eventually eliminate shin splints.
Groin Pull: Identifying and Managing
How can one recognize and effectively manage a groin pull, a common injury among athletes participating in high-intensity sports? Identifying a pulled groin often begins with recognizing sudden and severe pain in the groin area during or after physical activity. This is typically accompanied by swelling, muscle weakness, and difficulty in moving the leg. Pulled groin diagnosis is usually confirmed through physical examination and imaging tests such as ultrasound or MRI.
Once diagnosed, immediate treatment includes rest, ice, compression, and elevation (the RICE method). Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can also alleviate pain and reduce inflammation. However, effective long-term management involves a comprehensive rehabilitation program. Groin rehabilitation exercises play a crucial role in regaining strength and mobility and preventing reinjury. These exercises usually focus on strengthening the hip adductor muscles and improving overall flexibility.
Given the complexity of the groin area, recovery times vary. Some individuals may find relief within a few weeks, while others may require several months. It’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider before resuming sports activities to avoid exacerbating the injury. In conclusion, early diagnosis, immediate treatment, and a robust rehabilitation program are crucial in managing a groin pull effectively.
Concussions: Risks and Recovery
Shifting focus to another critical sport-related injury, concussions pose significant risks and require meticulous recovery processes to ensure a safe return to play. Concussions, often resulting from a blow to the head, can cause a range of short-term and long-term neurological issues. Early and accurate concussion diagnostics are vital in managing the injury and mitigating potential complications.
- Concussion Diagnostics: Modern diagnostic techniques combine physical examinations with neurocognitive tests to assess the severity of the injury. Advanced imaging technologies, like MRI and CT scans, offer detailed insights into the brain’s condition.
- Post-Concussion Syndrome (PCS): This condition may occur in the aftermath of a concussion, characterized by symptoms such as headaches, dizziness, and problems with concentration and memory. The syndrome can last for weeks to months after the initial injury.
- Recovery Process: The recovery process from a concussion requires rest and gradual return to normal activities. It’s essential to avoid strenuous physical and cognitive activities that can exacerbate symptoms.
Given the significant risks associated with concussions, it is crucial that athletes, coaches, and medical professionals understand the injury’s nature and the importance of proper recovery procedures.
Fractures: Types and Treatments
In the realm of sports injuries, fractures occupy a significant place due to their common occurrence and potential severity. It is critical to gain an understanding of the various types of fractures, as well as the treatments typically employed to address them. Moreover, preventative measures against these injuries should be thoroughly considered as a fundamental part of any sports health strategy.
Understanding Different Fractures
Delving into the realm of sports injuries, it is crucial to comprehend the various types of fractures and their corresponding treatments, a knowledge that can significantly aid in both prevention and recovery. Understanding fractures involves a grasp of their classification, the role of fracture nutrition in the healing process, and the impact of various treatments.
- Fracture Classification: Fractures are typically classified based on their location, the direction of the fracture line, and whether the skin is broken. Common types include transverse, oblique, and spiral fractures.
- Fracture Nutrition: Adequate nutrition is key to the healing process. A balanced diet rich in protein, vitamins C and D, and calcium, can expedite recovery.
- Impact of Treatment: The choice of treatment can significantly influence healing times and outcomes, ranging from immobilization to surgery.
Common Fracture Treatments
After gaining a comprehensive understanding of fracture classifications and the role of nutrition in healing, we now direct our attention to the various common treatments employed to manage and heal fractures. The fracture healing process is a complex and delicate endeavor, often requiring medical intervention. Traditional treatments usually involve immobilization with a cast or splint. However, these methods can sometimes lead to complications such as skin irritation, muscle atrophy, or joint stiffness. Recent advancements have introduced cast alternatives, such as functional braces or external fixators. These options allow for more mobility and comfort while still providing adequate support for healing. Each treatment is tailored to the specific type and location of the fracture, aiming to return the patient to their normal function as swiftly and safely as possible.
Preventing Sports Fractures
Understanding how to prevent sports fractures is a crucial aspect in the wider scope of injury management and treatment strategies. Preventive measures, which are multifaceted, largely involve lifestyle changes and proactive steps.
- Fracture nutrition: A well-balanced diet rich in calcium and vitamin D is essential for strong bones. Consuming dairy, green leafy vegetables, and fish can significantly decrease susceptibility to fractures.
- Bone density testing: Regular bone density tests can monitor bone health and preemptively identify risks of fractures. This allows for early intervention and the implementation of preventive measures.
- Physical activity: Regular, weight-bearing exercise helps strengthen bones and muscles, reducing the risk of sports fractures. However, it’s important to use correct form and equipment to avoid injury.
Following these steps can significantly reduce the occurrence of sports fractures.
Dislocations: Common in Contact Sports
Engaging in high-contact sports often leads to a prevalent and potentially debilitating injury known as a dislocation. Two of the most frequent ones encountered are shoulder and hip dislocations. These injuries occur when the ball and socket joint is forced out of its natural position, typically due to a strong impact or fall.
Shoulder dislocations are common in sports that involve throwing or hitting, such as baseball, rugby, or boxing. The powerful movements, often executed at high speeds, can result in the arm’s ball joint being forced out of the shoulder’s socket. The immediate result is severe pain and an inability to move the joint.
On the other hand, hip dislocations, although less common, are seen in contact sports like football or martial arts. They occur when an extreme force pushes the thigh bone out of the hip socket. This can be a result of a forceful tackle or a fall from a significant height.
In both cases, immediate medical attention is required to minimize damage and speed up recovery. It’s also crucial to strengthen the surrounding muscles with specific exercises as part of the rehabilitation process to prevent recurring dislocations.
Rotator Cuff Injuries: An Overview
Rotator cuff injuries, another peril athletes frequently face, primarily affect the group of muscles and tendons that provide stability and movement to the shoulder joint. The rotator cuff anatomy consists of four primary muscles: the supraspinatus, infraspinatus, teres minor, and subscapularis. These muscles work in synchrony to facilitate various shoulder movements, and any injury to this group can significantly impair the normal function of the shoulder.
These injuries typically manifest in three ways:
- Tendinitis: This is an inflammation or irritation of the tendons, often caused by overuse or acute trauma.
- Bursitis: This occurs when the bursa, a small fluid-filled sac that reduces friction between the rotator cuff and the shoulder blade, gets inflamed.
- Tears: These are the most severe form of rotator cuff injuries and can either be partial (damaging a part of the tendon) or complete (completely severing the tendon).
Surgical interventions may be required in severe cases, especially when complete tendon tears occur. The type of surgery depends on several factors, including the severity of the injury and the patient’s general health and age. The goal is always to restore as much function as possible and reduce pain.
Stress Fractures: Causes and Cures
Shifting our attention from soft tissue damage, we now delve into the realm of stress fractures, a common yet often overlooked sports injury that occurs primarily due to repetitive stress and overuse of a bone.
As the name implies, stress fractures are tiny cracks in bones caused by overworked muscles not being able to absorb added shock. When muscles tire, they transfer stress to bones, leading to these fractures. They are common in weight-bearing bones of the lower leg and foot, prevalent among athletes who participate in sports like basketball, tennis, and long-distance running.
Understanding running mechanics can provide insight into stress fracture risk. A faulty running technique can increase the likelihood of such injuries. For instance, overpronation (excessive inward foot roll) can place additional stress on specific bones, raising fracture risk.
Fracture nutrition is crucial in both the prevention and healing of stress fractures. A diet rich in calcium and Vitamin D strengthens bones, reducing fracture risk. Should a stress fracture occur, these nutrients aid in faster healing.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are Some Exercises to Improve Overall Flexibility and Potentially Prevent Sports Injuries?
Incorporating yoga benefits into a regular exercise routine can significantly improve overall flexibility. Additionally, implementing stretching routines before and after workouts aids in muscle recovery, potentially preventing future injury from strenuous physical activities.
How Does Diet Impact Recovery From Sports Injuries?
Diet significantly impacts recovery from sports injuries. Nutritional supplementation can aid in repairing damaged tissues, while preventing injury-related malnutrition. Balanced nutrition boosts the immune system, facilitating a faster and more efficient healing process.
Can Wearing Specific Types of Sports Gear Help Prevent Injuries?
Yes, gear selection can significantly impact injury statistics. Protective sports equipment, designed for specific activities, can minimize the risk of injuries by providing support and absorbing impact during strenuous physical activity.
Are There Any Age or Sex-Specific Sports Injuries That Are More Common?
Yes, injury statistics reveal age and sex-specific risk factors in sports. For instance, adolescent girls are more prone to anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) injuries, while older athletes often face degenerative injuries like tendinitis.
What Kind of Mental Health Support Is Available for Athletes Recovering From Sports Injuries?
Mental health support for athletes recovering from injuries often includes psychological counseling, injury coping strategies, and emotional rehabilitation. These methods aid in managing stress, anxiety, and depression during the recovery process.

