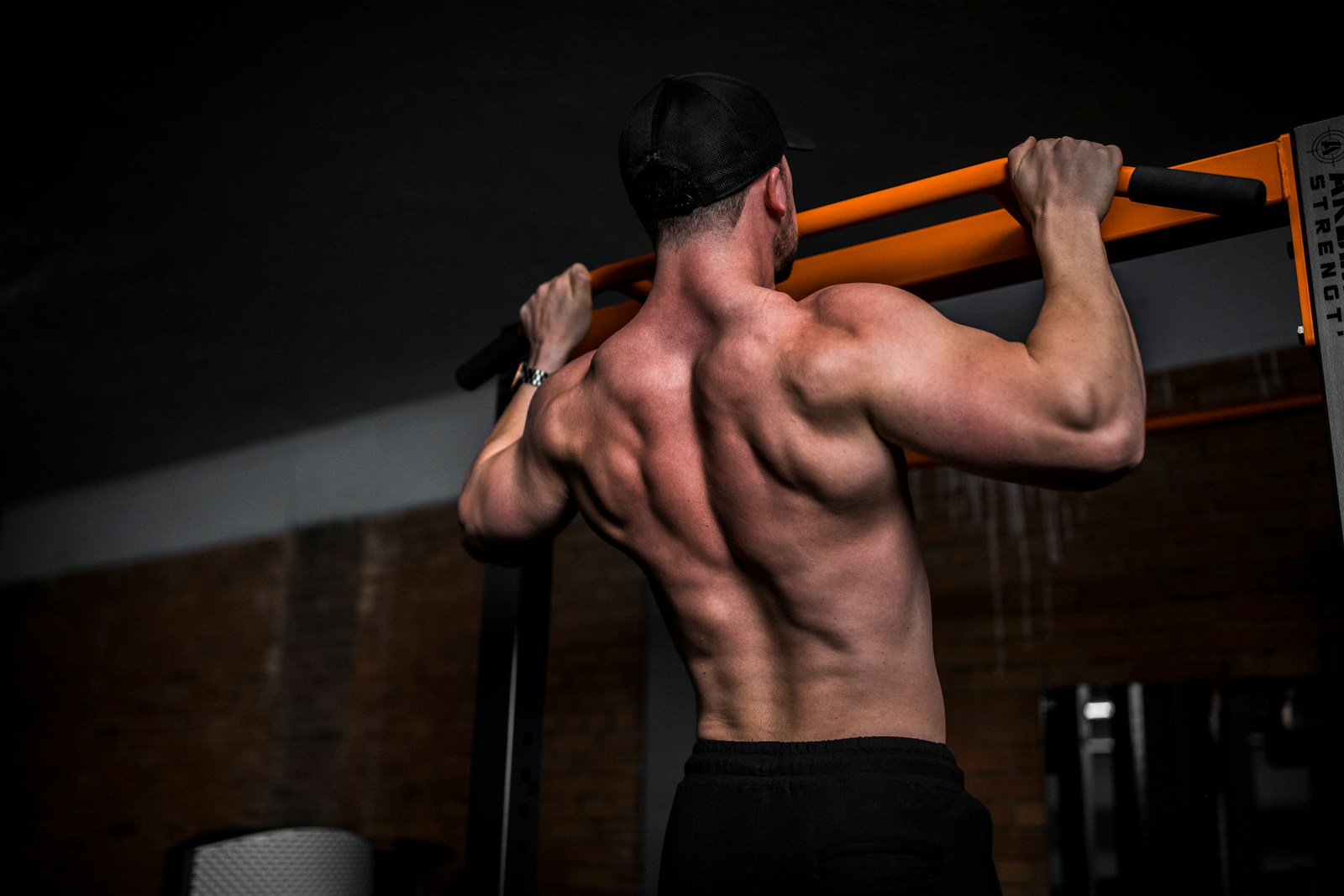
The intricate interplay of muscles in the upper back, consisting of the Trapezius, Rhomboids, and Latissimus dorsi, is a complex yet extremely important aspect of human physiology. These muscles contribute greatly to our physical stability, enable a variety of movements, and are instrumental in supporting the functions of the shoulder and neck. However, the implications of imbalances in these muscle groups can result in issues such as poor posture, chronic pain, and reduced mobility. What then, is the key to maintaining the health of these essential muscles? The answer lies in the right blend of strengthening exercises, flexibility routines, and everyday habits – a nuanced topic worthy of further exploration.
Understanding Upper Back Muscles
The complexity of the upper back muscles, comprising numerous interconnected and overlapping layers, necessitates a thorough and in-depth examination for a holistic understanding. These muscles, often overlooked, play a critical role in maintaining the structural integrity and balance of the human body.
Muscle imbalances in this region can have significant ramifications, leading to poor posture, chronic pain and mobility issues. Such imbalances typically result from a combination of factors including sedentary lifestyles, repetitive movement patterns, and inadequate physical conditioning. The upper back muscles, primarily responsible for the stabilization and movement of the shoulder blades and spine, directly influence the body’s posture. Any imbalance may cause a significant deviation from an ideal posture.
Posture correction, hence, becomes an integral part of addressing these muscle imbalances. A detailed approach that includes strength training, flexibility exercises, and ergonomic modifications can be instrumental in correcting the posture. It is also essential to note that each individual’s muscular structure is unique and hence, a personalized regimen is often required. This understanding of upper back muscles and their impact on posture and balance sets the foundation for the next subtopic, ‘Anatomy of Upper Back Muscles’.
Anatomy of Upper Back Muscles
Building on our understanding of the importance of upper back muscles, we now turn our attention to dissecting the intricate anatomy of these muscles, which comprise several key components each playing a distinctive role in our musculoskeletal system.
The upper back muscles, also known as the posterior thoracic muscles, are a complex network of large and small muscles that work together to support spine stability and facilitate movement. This anatomy is influenced by various factors, including the muscle aging process and posture’s impact.
The muscle aging process can affect the anatomical structure of these muscles. As we age, muscle fibers shrink in size and decrease in number, resulting in less mass and strength in the upper back muscles. This can lead to weakness, decreased mobility, and increased risk of injuries.
Posture’s impact on the anatomy of upper back muscles is equally significant. Poor posture can lead to muscle imbalances, where some muscles are overused and others are underused. This imbalance can lead to changes in the anatomy of these muscles, causing them to become tense, tight, or weak. This can contribute to upper back pain and other musculoskeletal issues. Understanding this anatomy can inform effective therapeutic interventions and preventive measures.
Major Muscles in the Upper Back
Delving into the complexity of the upper back, we find several major muscles playing crucial roles in facilitating movement and providing stability to the spine. The most prominent of these are the trapezius, the rhomboids, and the latissimus dorsi.
The trapezius, a large, flat, triangular muscle, extends longitudinally from the occipital bone to the lower thoracic vertebrae and laterally to the spine of the scapula. Its functions include moving, rotating, and stabilizing the scapula.
The rhomboids, located beneath the trapezius, are essential in retracting the scapula, contributing significantly to back posture correction. These muscles work in unison, and the importance of muscle symmetry cannot be understated.
The latissimus dorsi, the largest muscle in the upper body, spans from the lower back to the humerus. It plays a crucial role in the movement of the upper body, particularly in tasks involving pulling or lifting.
Functions of Upper Back Muscles
When evaluating the functions of the upper back muscles, it becomes clear that these structures play pivotal roles in a variety of movements and provide essential support for the spinal column. The upper back muscles are responsible for actions such as shoulder and neck movements, including rotation, flexion, and extension. They aid in the stabilization of the thoracic spine, contributing greatly to the maintenance of an upright posture.
The importance of muscle hydration in these functions cannot be overstressed. Hydration guarantees that the muscle fibers are flexible and resilient, reducing the risk of strains or tears. Adequate fluid intake facilitates the smooth contraction and relaxation of these muscles during activities, thereby enhancing their overall performance.
Furthermore, the benefits of posture correction are closely tied to the effective functioning of the upper back muscles. Correct posture involves the ideal alignment of the spine, which is highly dependent on the strength and coordination of these muscles. By supporting the spine and maintaining balance, the upper back muscles prevent undue stress on the vertebral discs. This leads to fewer instances of back pain and reduces the potential for long-term spinal complications. Hence, understanding the functions of upper back muscles is crucial for maintaining spinal health.
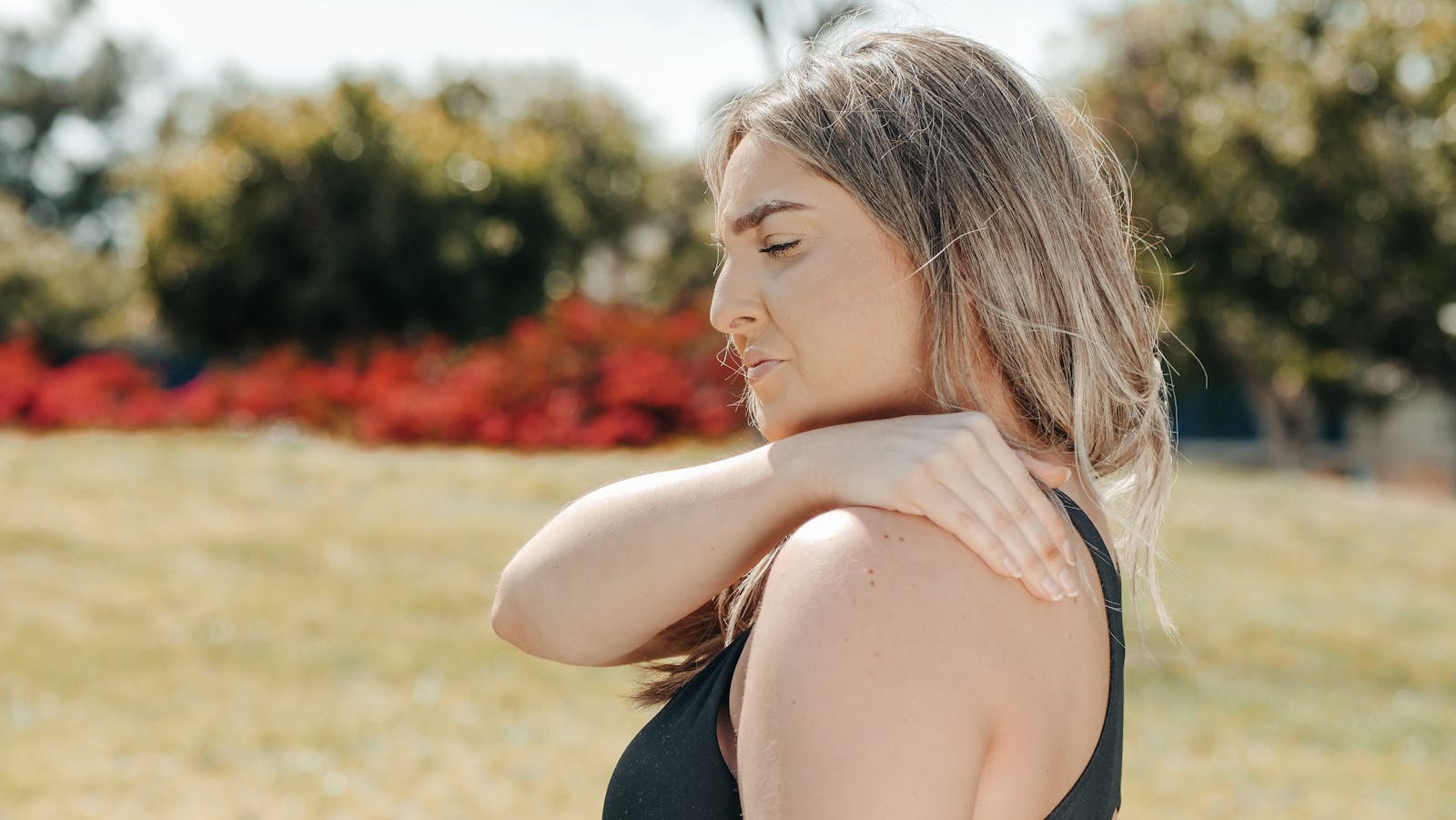

Common Upper Back Muscle Injuries
Upper back muscle injuries, commonly caused by strain or overuse, present a significant concern due to the critical role these muscles play in supporting the spine and maintaining posture. Identification of such injuries may require careful examination, given the complex anatomy of this region, which includes numerous muscles, ligaments and joints. Once diagnosed, treatment for these muscle strains will typically involve a combination of rest, physiotherapy and, in some cases, surgical intervention.
Identifying Upper Back Injuries
In the domain of physical health, it is of paramount importance to understand the various types of injuries that can afflict the muscles in the upper back, including common ones such as strains, sprains, and herniated discs.
- Strains: These injuries occur when the muscle fibers are overstretched or torn. Injury symptoms include pain, muscle spasms, and limited ability to move.
- Sprains: These injuries involve ligaments, the tissues that connect bones. Symptoms are similar to strains but may also include swelling.
- Herniated discs: This occurs when a disc in the spine ruptures, causing pain, numbness, or weakness.
- Fractures: These are breaks in the bones of the spine. Symptoms include severe pain and difficulty moving.
Rehabilitation methods for these injuries vary, but often include physiotherapy, medication, and rest.
Treatment for Muscle Strains
Finding the way to recovery following a muscle strain, especially in the area of the upper back, requires a thorough understanding of effective treatment strategies. One must consider the strain severity, as this directly impacts the required approach towards pain management. Minor strains often respond well to conservative treatments such as rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE). Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can also be employed to alleviate pain and reduce inflammation. Severe strains, however, might necessitate more intensive treatments like physical therapy or even surgery. Throughout the treatment process, it is critical to continuously monitor the patient’s progress, adjusting the treatment plan as necessary. By tailoring the treatment to the individual’s needs and the strain severity, optimal recovery outcomes can be achieved.
Causes of Upper Back Pain
Experiencing discomfort in the upper back can be attributed to a variety of causes, ranging from poor posture to more serious medical conditions. The scope of these causes can be broadly categorized into four main areas:
- Poor Posture: Lack of posture improvement can lead to muscle strain, causing upper back pain. This is typically seen in individuals who sit for extended periods, often in front of computers, leading to slouching and strain on the upper back muscles.
- Stress: Stress management, or the lack thereof, can also cause upper back pain. When we’re stressed, our bodies produce hormones that can cause muscle tension and spasms, particularly in the upper back.
- Overuse of Muscles: Excessive physical activity, or performing activities one is unaccustomed to, can lead to muscle strain or injury in the upper back area.
- Medical Conditions: Certain medical conditions such as osteoporosis, herniated discs, or spinal infections can directly cause upper back pain.
Understanding these causal factors is the first step towards managing the discomfort associated with upper back pain. The subsequent steps would involve the implementation of strategies to alleviate these causes, which will be discussed in future articles.
Preventing Upper Back Muscle Strain
To mitigate the risk of strain in the upper back muscles, a multifaceted approach encompassing regular exercise, proper lifting technique, and adequate rest is recommended. Regular exercise, specifically targeted at strengthening the muscle groups in the back, can enhance structural integrity and thereby reduce susceptibility to injury. Proper lifting techniques, including the appropriate use of the legs and core to bear load, coupled with sufficient rest and recovery periods, can further aid in the prevention of muscle strain in this critical region.
Importance of Regular Exercise
Regularly incorporating strength-building exercises into one’s routine greatly reduces the risk of straining the muscles in the upper back, thereby promoting peak muscular health and functionality. Exercise frequency is an important factor in this preventative strategy, as a sedentary lifestyle can lead to muscle weakness and consequently, strain.
- Regular exercise enhances muscle strength and endurance, reducing the likelihood of injury.
- Exercise frequency should be consistent, ideally 3-4 times per week, to prevent muscle deconditioning.
- Low-impact exercises such as swimming or yoga can help maintain muscle health without excessive strain.
- Regular stretching is essential to maintain flexibility and prevent muscle tightness, a common precursor to strain.
Proper Lifting Techniques
Implementing proper lifting techniques plays an essential role in preventing undue strain and potential injuries to the upper back muscles. One such technique involves lifting gear usage. This includes belts, gloves and weightlifting straps, which can provide support and stability, reducing the likelihood of muscle sprains. Equally important is posture correction. Maintaining a straight back, bending the knees and using the strength of your legs to lift can protect the upper back from excessive strain. Moreover, it’s important to avoid twisting or turning while lifting, as this can overstretch and damage the muscles. Lifting should be a smooth, controlled movement, with the weight close to the body to minimize stress on the back. These techniques, when properly executed, can greatly reduce the risk of upper back muscle strain.
Adequate Rest and Recovery
In addition to employing proper lifting techniques, allowing adequate time for rest and recovery is another effective strategy to prevent strain and injury to the upper back muscles. This recovery period is essential for the body to repair muscle tissue and replenish energy stores.
To guarantee a thorough rest and recovery process, consider these four points:
- Sleep importance: Sleep is when most muscle repair and growth occurs, so aim for 7-9 hours per night.
- Hydration benefits: Water helps transport nutrients to your muscles, promoting recovery.
- Active rest: Light activities such as walking can aid in muscle recovery by promoting blood flow.
- Nutrition: Consuming adequate protein helps repair and build muscle tissue, speeding up recovery time.
Exercises for Upper Back Strength
To enhance the strength and stability of the upper back muscles, it is crucial to engage in targeted exercises that focus on this particular area. A critical aspect of these exercises is posture correction, which is a fundamental technique needed to guarantee the effectiveness of the targeted workouts. A correct posture guarantees the upper back muscles are well-aligned, allowing them to work more efficiently and preventing undue strain.
Stretching benefits are also integral to strengthening the upper back muscles. Regularly engaging in stretching exercises promotes flexibility, reduces muscle tension, and enhances overall muscle health. One effective exercise is the ‘doorway stretch’, which targets the pectoral muscles that often pull the shoulders forwards, leading to poor posture. Another is the ‘cat-camel stretch’, which works out the entire spine and helps improve postural alignment.
Resistance training, such as dumbbell rows and lat pulldowns, also plays a significant role in upper back strength. These exercises challenge the muscles, leading to micro-tears that heal stronger, thereby increasing the muscle mass and overall strength. As with any exercise regimen, consistency, proper form, and progressive overloading are key to achieving the best results.
Treatment Options for Muscle Pain
Numerous effective treatment options exist for upper back muscle pain, ranging from thorough evaluations by healthcare professionals to determine the best course of action. These can include non-invasive therapies such as heat or cold applications and over-the-counter pain relievers to more complex interventions like physical therapy or surgery. Each treatment’s efficacy varies based on the type, severity, and duration of the pain, as well as the individual’s overall health status.
- Pain Medication Options: Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or acetaminophen, can alleviate minor to moderate upper back pain. For severe pain, prescription medications, including muscle relaxants, opioids, or corticosteroids, may be necessary.
- Physical Therapy: This involves exercises and stretches designed to strengthen the back muscles and increase flexibility. It can also include ultrasound therapy or electrical stimulation.
- Alternative Therapies: Techniques such as acupuncture, massage, chiropractic adjustments, and yoga have shown effectiveness in relieving upper back pain in some individuals.
- Surgical Intervention: This is usually the last resort and is considered when other treatments have failed, or if there is a serious underlying condition like a herniated disc or spinal stenosis.
Choosing the right treatment option should be based on a thorough evaluation by a healthcare professional, taking into account the patient’s specific symptoms, overall health, and lifestyle.
Importance of Upper Back Flexibility
Maintaining flexibility in the upper back muscles is crucial as it greatly influences the overall function and mobility of the spine, thereby playing a pivotal role in daily activities such as bending, lifting, and twisting. Peak flexibility in these muscles allows for a wider range of motion, enhances athletic performance, and reduces the risk of injury due to muscle strains or tears.
The benefits of flexibility, however, extend beyond physical prowess. Enhanced flexibility promotes better posture, reducing the likelihood of developing chronic conditions such as kyphosis (hunchback) and scoliosis. It also aids in the alleviation of muscle tension and stress, thereby contributing to overall well-being.
To take advantage of these flexibility benefits, stretching routines targeting the upper back muscles are recommended. These routines should ideally incorporate both static stretches, held for a given duration to increase muscle length, and dynamic stretches, involving controlled movements to improve range of motion. In doing so, they make sure that the muscles are adequately prepared for physical exertion while also facilitating recovery post-workout.
Maintaining Upper Back Muscle Health
Maintaining the health of the upper back muscles is dependent upon two key factors: regular exercise and appropriate nutrition. Exercise plays a vital role in enhancing muscular strength, endurance, and flexibility, while nutrition provides the essential macro and micronutrients for muscle growth, recovery, and overall health. A strategic combination of these elements can greatly contribute to the efficient functioning and longevity of upper back muscles.
Regular Exercise Importance
Engaging in regular exercise plays a pivotal role in preserving the health and flexibility of upper back muscles. When considering exercise consistency and workout intensity, it’s important to create a routine that adequately challenges these muscles while also promoting their longevity.
Here are four key benefits of regular exercise for upper back muscles:
- Strengthens Muscles: Consistent workouts enhance muscle strength and prevent muscle atrophy.
- Improves Posture: Exercise can correct posture issues, reducing strain and discomfort in the upper back.
- Enhances Flexibility: Regular movement maintains muscle flexibility, mitigating the risk of injuries.
- Promotes Muscle Recovery: A balanced workout routine, involving both high-intensity exercises and rest periods, promotes efficient muscle recovery and growth.
Thus, regular workouts are critical for maintaining healthy upper back muscles.
Nutrition for Muscles
In addition to regular exercise, proper nutrition also plays an important role in preserving the health and vitality of upper back muscles. Incorporating muscle building foods such as lean proteins, complex carbohydrates, and healthy fats into your diet can greatly enhance muscle health and performance. Proteins, for instance, provide the essential amino acids necessary for muscle repair and growth, while complex carbohydrates supply the energy required for strenuous physical activities.
Supplements can also be effective, provided they are used judiciously and in conjunction with a balanced diet. Nutritional supplements like protein powders, creatine, and branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs) may aid muscle recovery, growth, and strength. However, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any supplement regimen.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are the Symptoms of a Torn Upper Back Muscle?
Symptoms of a torn muscle may include pain, swelling, and limited range of movement, impairing muscle recovery. Proper injury prevention strategies can mitigate these symptoms and promote a more efficient healing process.
Can Poor Posture Affect Upper Back Muscles?
Yes, poor posture can detrimentally impact the body’s musculature. Implementing posture correction techniques and using ergonomic furniture can offer significant benefits, helping to maintain alignment and reduce the risk of muscle strain or injury.
What Role Does Nutrition Play in Upper Back Muscle Health?
Nutrition plays a vital role in muscle health. Specific dietary supplements can support muscle recovery and growth. Adequate protein, healthy fats, and certain vitamins are key for maintaining and improving muscular strength and functionality.
Can Stress or Anxiety Contribute to Upper Back Pain?
Yes, stress and anxiety can contribute to pain. Emotional strain effects can manifest physically due to the mind-body connection, leading to muscle tension, particularly in areas like the upper back, causing discomfort or pain.
How Does Aging Impact the Strength and Flexibility of Upper Back Muscles?
Aging can lead to natural deterioration in strength and flexibility. Exercise benefits these areas by combating age-related changes, particularly in the aging spine, to maintain or improve the overall health and functionality of muscles.

